“Metalworking lathes are necessary to the production of almost everything but are very expensive. In 1915, special lathes made from concrete were developed to quickly and cheaply produce millions of cannon shells needed for World War I.
Lucien Yeomans, the inventor, won the nation’s highest engineering award for it but sadly the technique was almost forgotten after the war. We re-discovered it as a way to quickly make inexpensive but accurate machine tools for use in developing countries and in trade schools and shops everywhere.”
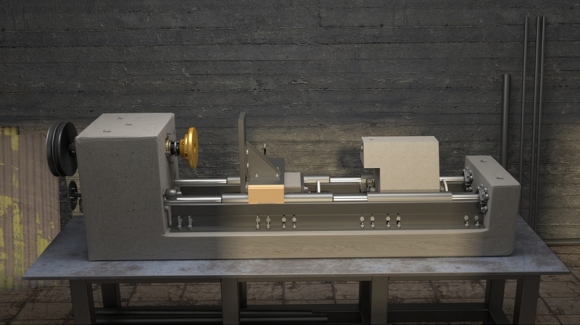
Pat Delany developed a metalworking lathe design that uses concrete parts cast in wooden molds to achieve high precision at a rock-bottom price of $150. Find the detailed building plans at Make Projects. Also check out Pat Delany’s low-cost DIY machine tools (such as a hand-powered drill and a treadle-powered generator), all built from recycled parts.