“The design of automobiles has tended toward insulation, offering an ever less involving driving experience. The animating ideal seems to be that the driver should be a disembodied observer, moving through a world of objects that present themselves as though on a screen. We have throttle by wire, brake by wire, and electrical assist (versus hydraulic assist) brakes, as well as traction control and anti-lock brakes that modulate our driving inputs for us. What all this idiot-proofing and abstraction amounts to is a genuine poverty of information reaching the driver.”
“What’s more, the information that does get through is presented in a highly mediated way, conveyed by potentiometers and silky smooth servos rather than by the seat of your pants. It is therefore highly discreet, and does not reflect fuzzy, subtle variations. Nor is it sensitive to changes that haven’t been anticipated and coded for ahead of time, for example the vibration that might arise from a brake caliper bracket that has come loose or cracked. Perhaps most troubling, the electronic mode of presentation means that information about the state of the car and of the road is competing with information from other electronic devices that may be a lot more interesting.”
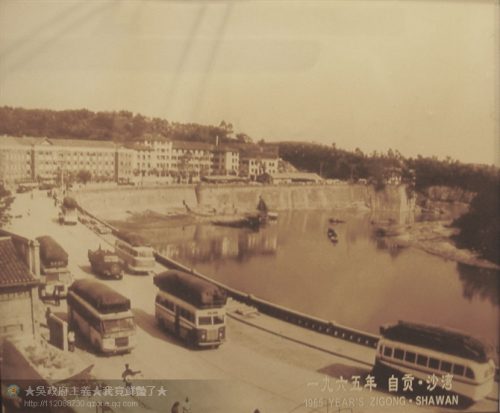
Read more: The Case for Dangerous Roads and Low-Tech Cars, Matthew B. Crawford. Picture credit.