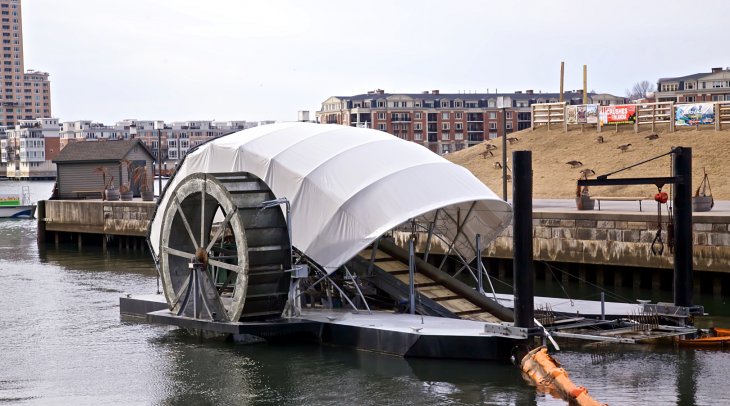
The Inner Harbor Water Wheel collects trash and debris at the outfall of the Jones Falls River, intercepting it before it enters Baltimore’s Inner Harbor, the Chesapeake Bay, and the Atlantic Ocean. Since it began operating, in May 2014, the water wheel has removed over 250 tons of trash from Baltimore’s waterways.
The machine funnels debris using two long booms and lifts it onto a wide conveyor belt. The refuse is then deposited in a dumpster on a separate platform. The wheel powers a conveyor, which lifts the trash from the river. When the current isn’t going quickly enough, the solar-powered pumps below the wheel push up water and get it spinning again.
The water wheel is part of the Waterfront Partnership’s Healthy Harbor Initiative, which aims to restore Baltimore’s Inner Harbor, making it swimmable by 2020. A second wheel is being crowdfunded.
See & read more: 1 / 2 / 3 / 4. Thanks to Tim Joye.
Related: Boat Mills