People made fire by hand for many thousands of years. We improved the energy efficiency of the process by letting the legs do the work. Unlike modern lighters, the lighter bike does not use fossil fuels. Lighting a cigarette takes about a minute of brisk pedaling.
No Tech Reader #40
- Out of the wild. [The New Atlantis] “The ideal of nature as it used to be before human intervention is one that Western urbanites created in the late nineteenth century, chiefly as a foil for their own modernity… This vision still permeates much of environmentalism and stands in the way of responsible action toward nature, particularly in the places where we actually live.”
- Minds on Fire: Cognitive Aspects of Early Firemaking and the Possible Inventors of Firemaking Kits. [Cambridge Archaeological Journal] “We analyse aspects of the two main hunter-gatherer firemaking techniques—the strike-a-light and the manual fire-drill—in terms of causal, social and prospective reasoning.”
- The Kayak’s Cultural Journey. [Craftsmanship Quarterly] “For millennia, Indigenous peoples across the world have built and used skin boats to fish and hunt, for sport and travel, even for warfare. Now non-Indigenous admirers of the craft are making them, too.”
- Permacomputing Aesthetics: Potential and Limits of Design Constraints in Computational Culture. [LIMITS 2023] “Permacomputing is a nascent concept and a community of practice oriented around issues of resilience and regenerativity in digital technology. At the heart of permacomputing are design principles that embrace limits and constraints as a positive thing, as well as being creative with available computational resources.”
- Building and Monitoring a SolarPowered Web Server. [ETH zürich] “In this thesis we focus on building a solar-powered web server. We present existing websites which are fully or partially solar powered, introduce some background about battery state of charge estimation and how to determine the right solar panel and battery size. Reusing components from older projects, we host a static website on an exemplary setup, which is solely solar powered.
No Tech Reader #35
- A hundred and nineteen things a punkist should know. [http://www.punk.ist]
- Firewood will save the West. [Unherd] “Our dysfunctional society must return to the hearth.”
- ‘Luddite’ Teens Don’t Want Your Likes. [NYT] “When the only thing better than a flip phone is no phone at all.”
- Papers and patents are becoming less disruptive over time. [Nature] “We find that papers and patents are increasingly less likely to break with the past in ways that push science and technology in new directions. Overall, our results suggest that slowing rates of disruption may reflect a fundamental shift in the nature of science and technology.”
- Assessing the effectiveness of energy efficiency measures in the residential sector gas consumption through dynamic treatment effects: Evidence from England and Wales. [Energy Economics] “This paper disentangles the long-lasting effects of energy efficiency technical improvements in UK residential buildings. The installation of energy efficiency measures is associated with short-term reductions in residential gas consumption. Energy savings disappear between two and four years after retrofitting by loft insulation and cavity wall insulation, respectively. The disappearance of energy savings in the longer run could be explained by the energy performance gap, the rebound effect and/or by concurrent residential construction projects and renovations associated with increases in energy consumption. Notably, for households in deprived areas, the installation of these efficiency measures does not deliver energy savings.”
- Mapping Four Decades of Appropriate Technology Research: A Bibliometric Analysis from 1973 to 2021. [Sains Humanika] “The purpose of the study is to examine the publication trends, collaborative structures, and central themes in appropriate technology studies.”
- Life in the Slow Lane. [Longreads] “Cooking all day while the cook is away. How the slow cooker changed the world.”
- Can a Robot Shoot an Olympic Recurve Bow? A preliminary study. [National Taiwan Normal University]
- Amnesty, Yes—And Here is the Price. [Charles Eisenstein] “The invisible workings of the Covid machine must be laid bare if we are to prevent something similar from happening again.”
- Reduce, re-use, re-ride: Bike waste and moving towards a circular economy for sporting goods. [International Review for the Sociology of Sport] “This study focuses on the bike and its role in global waste accumulation through various forms of planned obsolescence.”
- Civilian-Based Defense: A Post-Military Weapons System. [International Center on Nonviolent Conflict]
- Millionaire spending incompatible with 1.5 °C ambitions. [Cleaner Production Letters]
- Radical online collections and archives. [New Historical Express]
Chimneyless Houses
“Early shelters were built of availale materials. Hides spread over poles or the bones and tusks of mammoths formed a type widely used. Stone and clay were common early building materials. Usually there was only a single room, with the fire located at the center of the living area. In many parts of the world this pattern changed little from the earlies times right up to the present. Smoke escaped from such dwellings as it could, through the low door or a smoke hole in the roof… The Scots developed a special word, snighe, for rain that worked its way through the roof sods and dripped down black with soot upon the people below.” [Read more…]
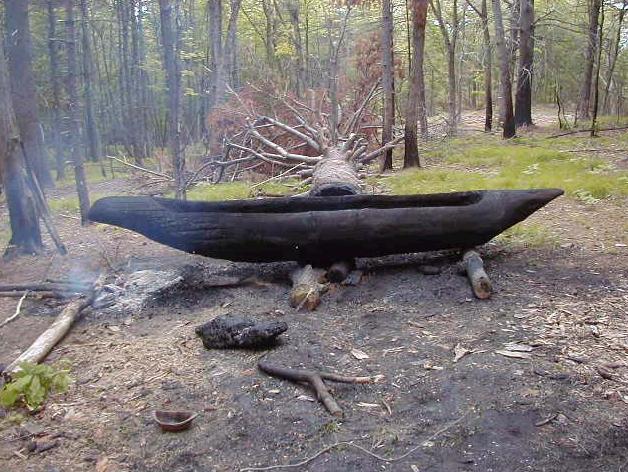
Making a Dugout Canoe Using Stone Tools and Fire
“The Dugout Canoe Project (.pdf) began as an experiment to use traditional Native American technologies. Archaeologists are reliant on just a few ethnohistoric sources that mention how Native Americans made dugout canoes using stone tools and fire. Numerous contemporary examples of dugouts exist, particularly Plimouth Plantation’s Wampanoag Indian Program, made by burning and scraping out logs. However, to the best of our knowledge, no one has attempted to fell a tree using only stone tools and fire. We wanted to see if we could cut down a live tree using these technologies, something that may not have been done in this area for several hundred years.”
“Dugout canoes are probably the first type of boat ever made. People from all over the world made dugouts. They were widely used in North America before the arrival of Europeans. Dugout canoes were made by Native Americans across North and South America for transportation and to hunt fish with a spear, bow and arrows, or with hooks made from antler or bones. In Eastern North America, dugout canoes were typically made from a single log of chestnut or pine. Carefully controlled fires were used to hollow out these logs. The fires were extinguished at intervals to scrape out the burned wood with wood, shell or stone tools, giving the canoes a flat bottom with straight sides.”
Courtesy of the Fruitlands Museum. More posts on primitive technology.