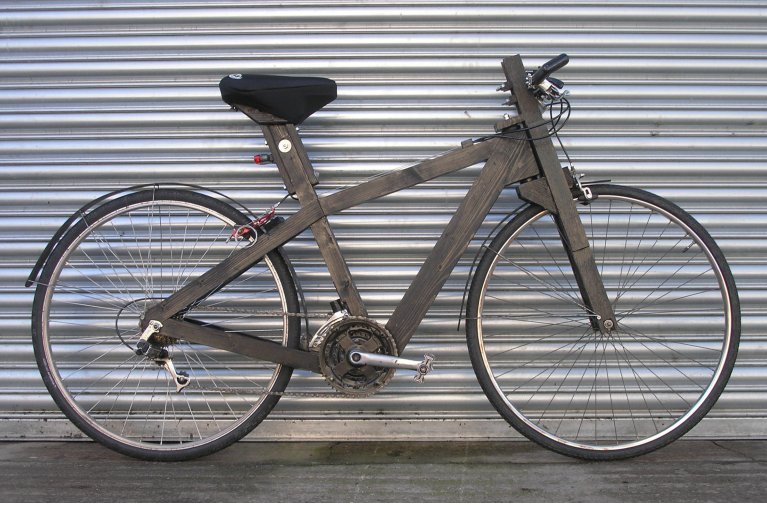
The Ironwood bicycle is a wooden framed bike that people could make themselves with commonly available materials. It has a laminated wooden frame and fork to which standard bicycle components are bolted. The frame can be made with basic carpentry and metalwork skills, without the need for welding or soldering. The design is intended for small scale bicycle production that would support local employment as an alternative to importing bicycles from around the world. More: http://www.ironwoodbicycle.com.
No Tech Reader #42: Transportation
Ticket prices of planes versus trains in Europe (pdf). [Greenpeace] “By analysing 112 European routes and comparing air and rail fares on 9 different days for each route, this report shows the extent to which European citizens are being encouraged to fly. It also identifies the reasons for these outrageous price differences and proposes solutions to make rail competitive on all routes.”
Crosswalks and pedestrian safety: What you need to know from recent research. [Journalist Resource]
The relationship between cycle track width and the lateral position of cyclists, and implications for the required cycle track width. [Journal of Safety Research] “Given a cyclists’ lateral position while meeting, common variations between cyclists’ steering behavior, and vehicle width and circumstances, a cycle track width of 250 cm is needed for safe meeting maneuvers.”
“Electric Vehicles”: Arthur Berman, Simon Michaux & Pedro Prieto. [The Great Simplification] “Are current EV initiatives taking a science-based systems approach towards this massive economic, environmental, and cultural shift or are they rooted in energy blindness?”
Retro Style Velomobiles (video). [Glowing Ray] “Velocar was the name given to velomobiles made in the 1930s and 1940s by Mochet et Cie of Puteaux, France and colloquially to the company’s recumbent bicycles.”
No Tech Reader #35
- A hundred and nineteen things a punkist should know. [http://www.punk.ist]
- Firewood will save the West. [Unherd] “Our dysfunctional society must return to the hearth.”
- ‘Luddite’ Teens Don’t Want Your Likes. [NYT] “When the only thing better than a flip phone is no phone at all.”
- Papers and patents are becoming less disruptive over time. [Nature] “We find that papers and patents are increasingly less likely to break with the past in ways that push science and technology in new directions. Overall, our results suggest that slowing rates of disruption may reflect a fundamental shift in the nature of science and technology.”
- Assessing the effectiveness of energy efficiency measures in the residential sector gas consumption through dynamic treatment effects: Evidence from England and Wales. [Energy Economics] “This paper disentangles the long-lasting effects of energy efficiency technical improvements in UK residential buildings. The installation of energy efficiency measures is associated with short-term reductions in residential gas consumption. Energy savings disappear between two and four years after retrofitting by loft insulation and cavity wall insulation, respectively. The disappearance of energy savings in the longer run could be explained by the energy performance gap, the rebound effect and/or by concurrent residential construction projects and renovations associated with increases in energy consumption. Notably, for households in deprived areas, the installation of these efficiency measures does not deliver energy savings.”
- Mapping Four Decades of Appropriate Technology Research: A Bibliometric Analysis from 1973 to 2021. [Sains Humanika] “The purpose of the study is to examine the publication trends, collaborative structures, and central themes in appropriate technology studies.”
- Life in the Slow Lane. [Longreads] “Cooking all day while the cook is away. How the slow cooker changed the world.”
- Can a Robot Shoot an Olympic Recurve Bow? A preliminary study. [National Taiwan Normal University]
- Amnesty, Yes—And Here is the Price. [Charles Eisenstein] “The invisible workings of the Covid machine must be laid bare if we are to prevent something similar from happening again.”
- Reduce, re-use, re-ride: Bike waste and moving towards a circular economy for sporting goods. [International Review for the Sociology of Sport] “This study focuses on the bike and its role in global waste accumulation through various forms of planned obsolescence.”
- Civilian-Based Defense: A Post-Military Weapons System. [International Center on Nonviolent Conflict]
- Millionaire spending incompatible with 1.5 °C ambitions. [Cleaner Production Letters]
- Radical online collections and archives. [New Historical Express]
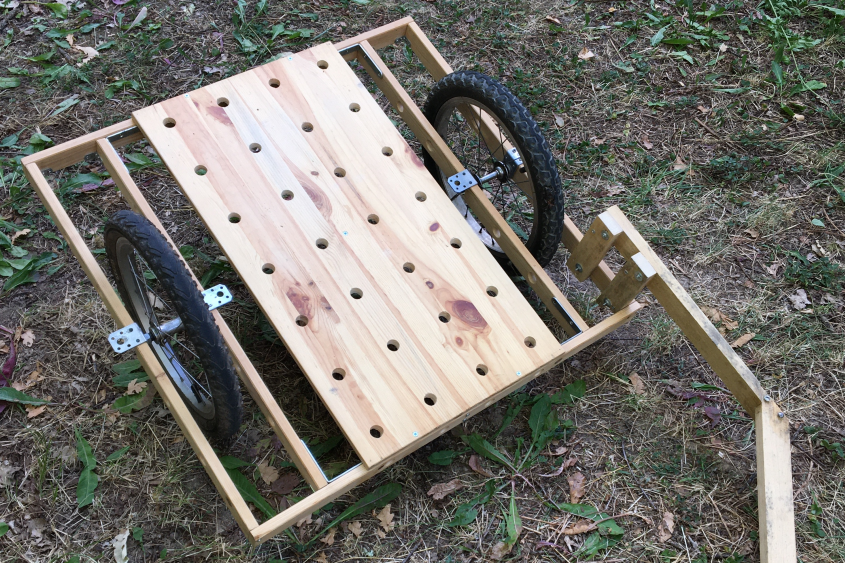
DIY Wooden Bike Trolley
Marie Verdeil made a tutorial for a simple wooden bike trolley. It is available in English and French on the Low Tech Lab wiki.
Method to create a simple bike trolley, using up-cycled materials. Easily fixated to every bike (adult size). Holes on the board help attach any kind of cargo. It’s made out of wood and simple hand tools, no welding required. Dimensions are detailed and can easily be adapted to the material available.
I tried to create a trolley, which can replace the car to go to the market / grocery shopping. No need to transport heavy cargo, but big objects (cardboard boxes, crates, wood, etc.) – Therefore it needs to be easily adaptable, with the option to fix a crate on the board. + Priority goes to second-hand materials!
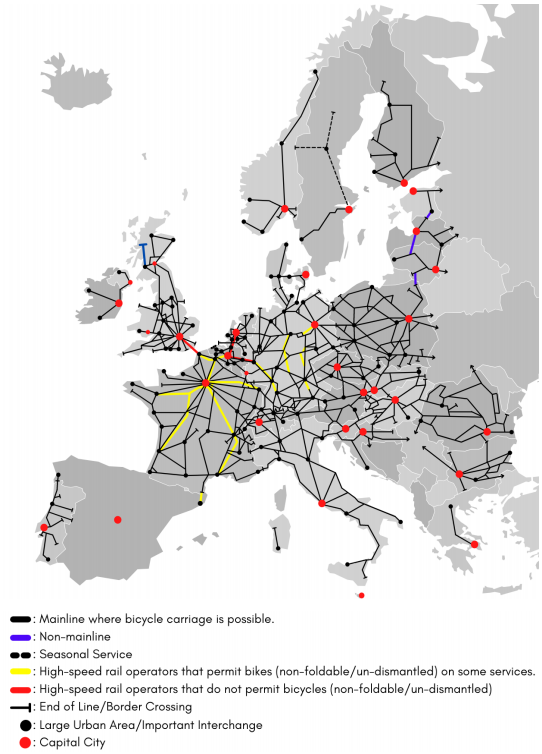
The bicycle friendliness of European railway operators
The European Cyclists’ Federation (ECF) has released a new report, “Cyclists love trains: An analysis of the bicycle friendliness of European railway operators,” which aims to guide industry and policymakers in identifying ways to improve the combination of two of the most sustainable modes of transport: bikes and trains.
This timely new report analyses and ranks 69 European train companies and services according to six key indicators for combined bike-and-train travel, such as bicycle spaces in trains and the quality of bike ticket or reservation channels. The report’s rankings show that there is much room for improvement in Europe.
Only one train service, NS-DB (Intercity Berlin), which runs between Amsterdam and Berlin, scored in the “excellent” category. Operators that scored in the “good” category in facilitating bike-and-train travel include SNCB/NMBS, SBB, Deutsche Bahn and MÁV-START.
One fourth of the 69 operators and services scored in the “moderate” category, including České dráhy, SNCF and Trenitalia, while the rest perform either “poorly” or “very poorly” on most indicators, including Flixtrain, Greater Anglia, Renfe and Eurostar.
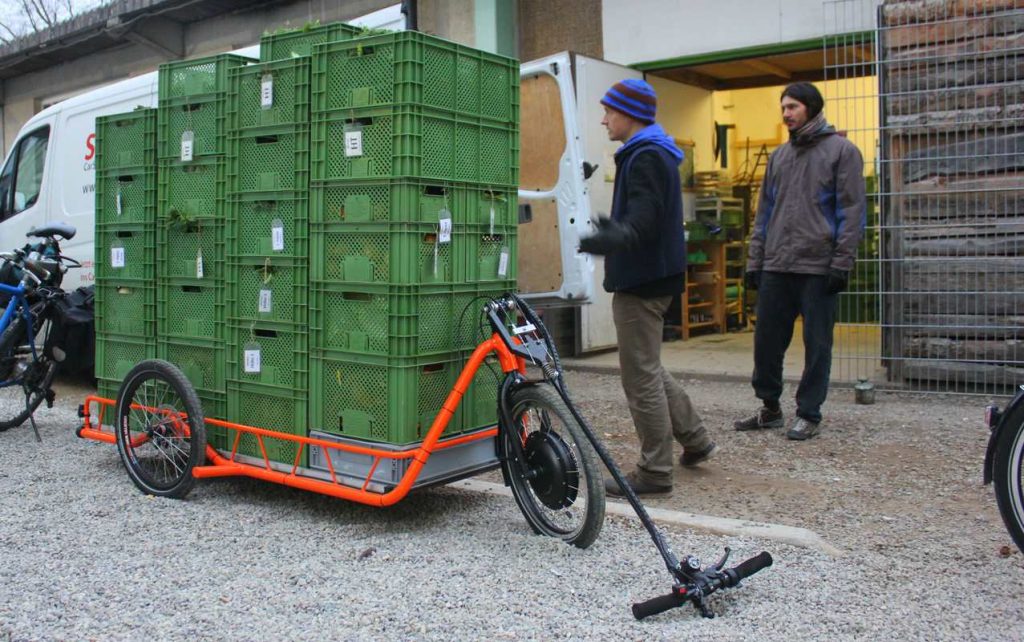
Electrically Powered Bicycle Trailer & Hand Cart (DIY)
The German-made Carla Cargo is a three-wheeled cycle trailer with an electric assist motor. It can be pulled by any type of bicycle (including a cargo cycle or an electric bike), and it allows you to carry heavy (up to 150 kg) and bulky cargo (a loading platform of 60 x 160 cm). Uncoupled from the bicycle, the Carla Cargo works as a hand cart for large or heavy loads. The vehicle weighs 40 kg including the battery, and has a range of 40 to 60 km.
 The electric motor is built into the front wheel and can produce 250 watts as a trailer (up to 23 km/h), and 500 watts as a handtruck (up to 6 km/h). The lithium-ion battery has a capacity of 11 or 15 Ah. The vehicle has two disk brakes and a parking brake, which are controlled via the handle or the bicycle handlebar.
The electric motor is built into the front wheel and can produce 250 watts as a trailer (up to 23 km/h), and 500 watts as a handtruck (up to 6 km/h). The lithium-ion battery has a capacity of 11 or 15 Ah. The vehicle has two disk brakes and a parking brake, which are controlled via the handle or the bicycle handlebar.
The Carlo Cargo sells for about 4,000 euro. The construction manual is freely accessible online, but only in German for now. The trailer/handcart is present at the International Cargo Bike Festival, April 16-17, in Nijmegem, the Netherlands.
Previously: 8-wheeler cargo cycle.